Today we are going to discuss on number of ways to Create a Service Order in SAP Customer Service or After sales processing
Businesses are more Oriented to Customer Satisfaction and this is needed to get success for any kind of Industry, Be it a Automobile, High-Tech, Heavy Equipment Manufacturer , whatever so ever.
When a company sells a product, we do expect a Service or Repair in service Industry
We identify a product , if it is repairable or serviceable by tracking it using SERIALIZATION
Repair of the material can be handled in SAP under CS module Using service Order functionality
But how a service Order can be created in SAP ????
There are different way to create a service Order, it depends on the process or scenario we use
1. REPAIR AT SITE:
>>>>This is the process where a Product is sold to customer and customer identifies some fault in its operation or certain functionalities are not working as per the specification. In such case , customer calls CIC ( customer Interaction center) where a Help Desk will be informed . A Customer Representative from Help Desk will ask Customer to bring the material to the Workshop or Plant where it can be repaired.
In this process, as per the process ,
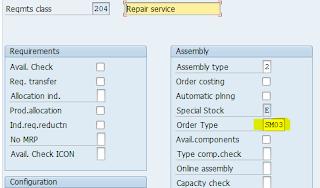
A repair Item ( IRRP) from the standard will trigger a Service Order. This setting lies in the Configuration
Item Category-->Determines Requirement type--> Requirement types determines-->Requirement Class.
Requirement class has the service Order type which should be created upon saving Repair Item
2. FIELD SERVICE PROCESS:
>>>>>This process triggers when a Field service Technician is planned to visit customer to get the issue resolved. In this case a service Notification and from it a service Order is created with service Order option
IW52--->IW32
3. ANNUAL MAINTENANCE CONTRACT:
>>>> this is a process which triggers from Contract and customer will take AMC during Contract for specific services and components. This process is triggered from Maintenance Plan which schedules service Order Creation automatically or a manually intervention is also possible
We use IP30 to set Maintenance Plan to Create Auto service Order and IP19 is used to report generated service Orders
4. SUB -SERVICE ORDER
>>>We use IW36 to create a ub-Order from Main service Order . this process triggers if there is any change in service activities or Task List triggered in Main service Order. In order to process new service request with reference to Main service Order a sub service Order is created
5. standalone service Order:
>>>> This is not a common Practice to create a standalone service Order, but when a field service Technician at customer visit identifies a spare part is damaged and he want it to be delivered to the customer ( in SAP) , then with reference to PO a service Order is created without a service notification
Use directly IW31
Hope it is useful for understanding basic ways of Creating service Order


keep it up
ReplyDeleteDelivery based transportation requirement number in TM will be the same as inbound and outbound deliveries number?
ReplyDelete